Background Scripts |
In this screen you can register and change background scripts. Open Form
Open Form
With the help of background scripts management processes and other time-consuming manual processes can be automated.
An example of a background script that automated an administrative process, is ‘BUBS_EMPTY_INTERFACES’. With this script the contents of the ERP interface tables are removed.
If a background script requires parameters for processing they can be specified in the part of the screen with the name ‘Script Parameters’.
The registration of background scripts is a typical activity for application developers. See the warning under Application Development.
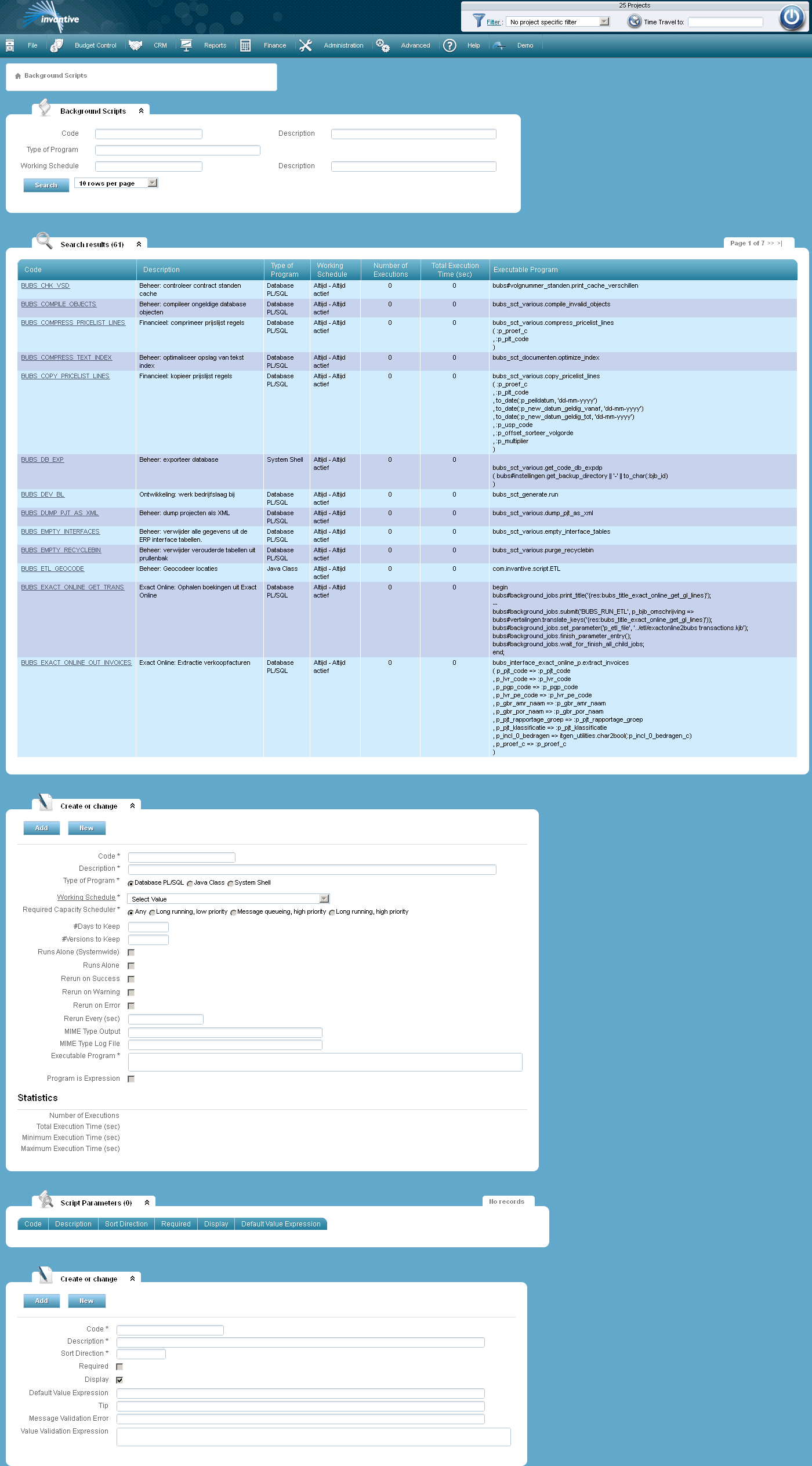
The meaning of the entry fields is:
Code |
The unique code of the script. |
Description |
The description of the script. |
Type of Program |
The type of program, including: •Oracle PL/SQL; for executing database packages, ideally suited for database changes. •JJava Class; for executing a Java program, ideally suited for executing mathematically intensive or non-database processes. •System Shell; for executing everything that cannot be executed as Oracle PL/SQL or Java class. |
Required Capacity Scheduler |
The required skills of the scheduler to be allowed to process background jobs based on this script. |
# Days to Keep |
The minimum amount of days after which the background jobs based on this script may be automatically removed. |
# Versions to Keep |
The minimum amount of versions after which the background jobs based on this script may be automatically removed. The oldest versions are deleted first. |
Runs Alone |
The maximum number of simultaneously running background jobs based on this script is only one, when checked. |
Rerun on Success |
A successfully completed background job based on this script will automatically start again when checked. |
Rerun on Warning |
When a background job based on this script was completed with a warning, it will automatically start again when checked. |
Rerun on Error |
When a background job based on this script was completed with an error based on this script it is automatically restarted when checked. |
Rerun Every (sec) |
The amount of time in seconds after which a background job based on this script will automatically be requested, if one of the options ‘Rerun on Success ’, ‘Rerun on Warning’ and/or ‘Rerun on Error’ is checked. |
MIME Type Output |
The MIME type of the output of this script, for example ‘text/html’. |
MIME-type Log File |
The MIME type of the log output of this script, for example ‘text/html’. |
Executable Program |
The name of the executable program or the code of the script to be executed in case of Oracle PL/SQL.
The following variables in the code are replaced by their respective values during the execution of the background script as a background process: •:bjb_id: ID of the background process. •:bjb_seq: number of the background process. •:sdr_code: code of the background planner. •:sdr_omschrijving: description of the background planner. •:gbr_naam: user that requested the background process. |
Program is Expression |
Indicates that the program text is a SQL expression when checked |
Code |
The unique code of the script parameters. |
Description |
Description of the script parameters. |
Sort Order |
Numerical value that determines the order in which the script parameters will appear in an entry form. |
Required |
Indicates if it is obliged to specify a value for the script parameter. |
The meaning of the other fields:
Number of Executions |
The total amount of finished background jobs that were based on this script. |
Total Execution Time (sec) |
The total time in seconds that background jobs have run, based on this script. |
Minimum Execution Time (sec) |
The minimum time in seconds that a background job has run, based on this script. |
Maximum Execution Time (sec) |
The minimum time in seconds that a background job has run, based on this script. |
Scripts of the category ‘System Shell’ are executed with the applicable system shell (command.com for Windows 95, cmd.exe for other Windows versions and /bin/ksh for UNIX and Linux).
 Invantive Estate
Invantive Estate